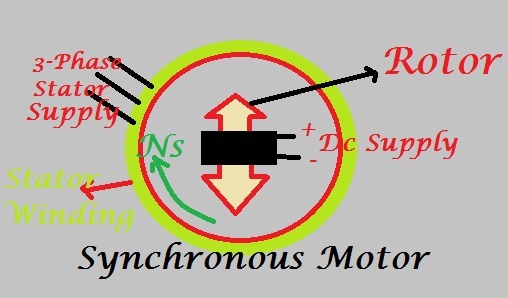
What is Synchronous Motor (सिंक्रोनस मोटर)
Synchronous Motor is a type of three-phase AC motors which run at synchronous speed
- A three-phase stator
almost like that of an induction motor. Medium voltage stators are often used. - Field excitation is provided on the rotor by either permanent magnet or electromagnets with number of poles equal to the poles of the RMF caused by stator.
- Synchronous motors works on the principle of magnetic locking between rotor magnetic field and stator magnetic field(RMF).A wound rotor (rotating field) which has the same number of poles as the stator, and is supplied by an external source of
DC . - Both brush-type and brushless exciters are supplied by the DC source. The rotor current establishes a north/south magnetic pole relationship in the rotor poles enabling the rotor to “lock-in-step” with the rotating stator flux.Once the magnetic locking occurs,synchronous motors will run at synchronous speed in accordance with the formula:Ns=120f/p
- But if the rotor has not got any initial rotation and the speed of stator magnetic field is very high then the situation is different.
- N pole of RMF will obviously gets attracted to S pole of rotor and will start to move in same direction.But since rotor has got some inertia this starting field will be very low.
- By this time the S pole of the RMF will be replaced by the N Pole. So it will give repulsive force.Therefore, rotor will be unable to start. Therefore, synchronous motor is not self starting.
- There are different methods of starting of synchronous motor which are as below:-i).Motor Starting by Reducing the supply Frequency ii)Motor Starting with an External Motor) iii)Motor Starting by Using damper (Amortisseur) Winding
2. Motor Starting with an External Motor:- The method of starting a synchronous motor is to attach an external starting motor (pony motor) to it and bring the synchronous machine to near about its rated speed .In this type of motor a prime mover can be used to start this motor i.e an external motor can be used to start this motor.
 |
| Image Source-Google Image by-https://www.slideserve.com |
VT= IaRa+jIa(Xl+Xas)+Ef
= IaRa+jIaXs+Ef
VT= Ia(Ra+jXs)+Ef
Phasor diagram of a synchronous motor (Lagging power factor load) :-
Based on equivalent circuit diagram and voltage equation VT= IaRa+jIaXs+Ef, phasor diagram can be drawn as,
 |
| Image Source-Google Image by-https://www.slideserve.com |
Let a synchronous motor is driving at constant torque load.
The active power(P) is constant, since the load and speed are constant. Thus,

Based on above equation and assumption if we draw the phasor diagram at three different excitation voltage we get,
 |
| Image Source-Google Image by-https://www.slideserve.com |
How to solve Numerical of three phase synchronous motor?Step by step process:
Above figure shows the effect of change in field excitation on the operation of the synchronous motor. As the field current is hanged, the tip of armature current phasor Ia will follow the locus in such a way that Ia cosØ remains constant (a line perpendicular to x=axis),
Overexcitation region: Suppose the synchronous motor is initially overexcited (in other words, excited with a large field current) and is operating at point above the x-axis , as shown in above Figure. The corresponding armature current Ia3 is leading V, and hence the input power factor is leading.
Unity power factor: Reduction of field current causes the tip of Ef phasor to move towards point Ef2: the armature current decreases to a minimum (Ia2) and the motor input power factor increases to unity.
Under excitation region: Further reduction of field current causes Ef to move to point Ef1: The armature current increases to Ia1 and the input power factor becomes lagging.
Synchronous motor V-curves: When the synchronous motor operates with constant power input, the variation of armature current (Ia) with field current is thus a V-shaped curve, as illustrated in Figure below. In general, overexcitation will cause the synchronous motor to operate at a leading power factor, while under excitation will cause the motor to operate at a lagging power factor. When the synchronous motor operates with constant power input, the variation of power factor with field current is thus a inverted V-shaped curve, as illustrated in Figure below.
In general, overexcitation will cause the synchronous motor to operate at a leading power factor, while under excitation will cause the motor to operate at a lagging power factor. Thus it can concluded that synchronous motor has variable-power- factor characteristic.
Differences between 3-phase synchronous motor and 3-phase induction motor are as follows:- 1.Synchronous motor always runs at a speed equal to its synchronous speed.Induction motor never runs at synchronous speed. 2.Synchronous motors require an additional DC power source for energizing rotor winding.Induction motors require only one power source.
3.Slip rings and brushes are required in synchronous motors,slip rings and brushes are not needed in induction motors (except SRIM)
4.Synchronous motors require additional starting mechanism. No starting mechanism is needed in induction motors.
5.The power factor of a synchronous motor can be adjusted to lagging, unity or leading by varying the excitation,Induction motor always runs at lagging power factor. 6.Synchronous motors are generally more efficient and more costlier.Induction motors are less efficient and less costlier.
|



